Sweeteners

This non-caloric sweetener is toxic and does not help you lose weight
Accidently discovered in 1965, this non-nutritive sweetener (N-L-alpha-Aspartyl-L-phenylalanine methyl ester (C14H18N2O5)) is 180-200 times sweeter than sugar. Although it has 4 calories /g it is used in very small quantities, so is virtually calorie free. Sold as Nutrasweet® in the little blue packets (also contain dextrose with maltodextrin), Equal original® , Canderel® , Spoonful® , Natrtaste blue® and other brands;
Having a somewhat bitter aftertaste, it is added to: beverages, cereals, yogurt, frozen and gelatin desserts, candy, sugar-free gum, juices, diet sodas, vitamin supplements, laxatives and more.
Aspartame is fully metabolized in the intestines. It is hydrolyzed to 50% phenylalanine, 40% aspartic acid (aspartate), and 10% methanol.
Phenylalanine blocks the brain's serotonin and dopamine production. After consuming aspartame, phenylalanine affects transporters in the blood brain barrier (BBB) blocking the transport of essential amino acids to the brain, necessary for the synthesis of the neurotransmitters dopaminE and serotonin in the central nervous system (CNS).
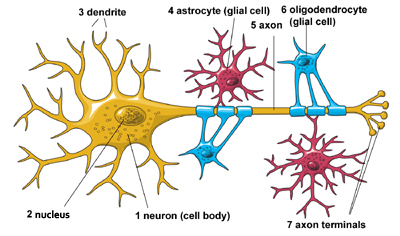
A neuron and its supporting glial cells (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes)
Aspartate, present in excess as a metabolite of aspartame, is neurotoxic by being a substrate for glutamate. This amino acid is a neurotransmitter used by nerve cells to send signals to other cells. It is used by every major excitatory function in the brain, accounting for > 90% of its synaptic connections. Acting on certain receptors, excess glutamate leads to hyperexcitability of cells, release of free radicals/oxidative stress and neuronal degeneration. Initially astrocytes (neuron supporting glial cells) are the protectors of neurons, but eventually, with an excess of glutamate in the extracellular space, they are activated and release toxic substances leading to the degeneration of both neurons and astrocytes.
Excitotoxicity due to excessive glutamate release and impaired uptake from the extracellular space is associated with stroke, autism, some forms of intellectual disability, and diseases such as ALS and Alzheimer's disease. References at Wikipedia Glutamate transporters, EAAT and VGLUT, found in membranes of neurons and glial cells (neuron support cells), normally rapidly remove glutamate from the extracellular space. Conversely, in brain injury or disease, excess glutamate can accumulate outside cells. This causes calcium ions to enter neurons, leading to neuronal damage and eventual cell death, a process called excitotoxicity.
Methanol contained in aspartame is insufficient to bring about alterations in the CNS. After consumption of aspartame, methanol is converted to formaldehyde and then to formic acid. Metabolic acidosis occurs with the accumulation of formate, which may eventually cause CNS depression, coma and death from respiratory system paralysis. However, after extensive evaluation based on metabolism studies, Butchko et al concluded that it is not possible for a human to ever consume enough aspartame in products to raise blood formate concentrations.
The latest studies show that the aspartame metabolite - diketopiperazine contributes to the formation of tumors in the CNS. E.g. gliomas, medulloblastomas and meningiomas. Glial cells are the main source of tumors, which can be caused by the use of the sweetener aspartame, as well as other substances.
Non-nutritive artificial sweeteners (NAS) toxic to gut bacteria increasing risk of prediabetes
Non-nutritive Artificial Sweeteners (NAS) cause weight gain!